Imagine moving to a country like Italy or Japan with only a basic grasp of the local language. Now, picture yourself in an unfamiliar city, suddenly experiencing sharp chest pain. You rush to the nearest hospital, heart pounding, only to realize no one there speaks English. The doctors ask questions, but you don’t understand them. You try to describe what you’re feeling, but the words won’t come. Panic sets in—not just from your condition, but from the helplessness of being unable to communicate.
Then, a nurse hands you a critical medical form you don’t understand—except for the signature line. Would you sign it? What if it was a consent form for a risky procedure or an unfamiliar medication? Would you trust that the medical staff fully understood your needs and were delivering proper care?
For millions of individuals in the U.S. with Limited English Proficiency (LEP), this is not just an unsettling hypothetical — it’s a daily reality. Every day, LEP individuals navigate a healthcare system designed for English speakers, where misunderstandings can mean the difference between the right diagnosis and the wrong one, between timely treatment and dangerous delays.
Their challenge raises an important question: How can we build a more inclusive system, ensuring that language is never a barrier to critical services?
Limited English Proficiency in the U.S.: The Facts
The U.S. is one of the most linguistically diverse countries in the world, with nearly 22% of the population speaking a language other than English at home. According to U.S. Census data, the most spoken non-English languages include Spanish (60.4%), Chinese (5.1%), Vietnamese (2.3%), and Tagalog (2.5%), reflecting the nation’s diverse linguistic landscape. The “Other Languages” category, which represents 22.8% of the population, includes German, Haitian, Portuguese, Hindi, Italian, Polish, Japanese, Persian (Farsi/Dari), Gujarati, Telugu, Bengali, Urdu, and many other less commonly
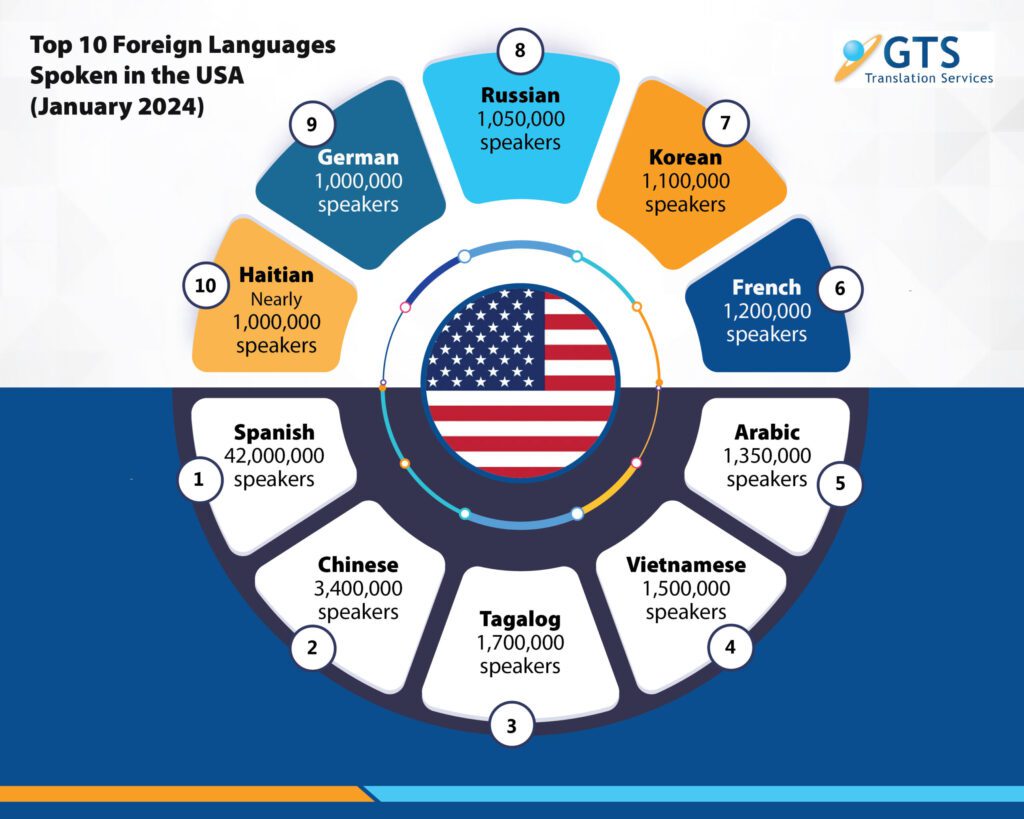
Image source: GTS Translation Services Blog
Not only are diverse languages spoken at home, but also approximately 25.7 million people in the U.S. have LEP, meaning that English is not their primary language, and they have limited ability to read, write, speak, or understand English.
For these millions of individuals with LEP, navigating essential services such as healthcare, education, financial institutions, and legal systems presents significant challenges. Language barriers can lead to miscommunication, misinformation, and limited access to critical resources, ultimately impacting quality of life and economic mobility.
The Hidden Cost of Language Access in Healthcare
Language barriers in healthcare can lead to significant challenges for LEP individuals. Studies indicate that nearly half of LEP patients experience difficulties in accessing medical services, which can result in delayed treatment, misdiagnoses, or misunderstandings of medical instructions. These barriers not only contribute to worsened health outcomes, but also increase healthcare costs due to prolonged hospital stays, higher readmission rates, and preventable complications.
Research from the Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF) shows that LEP individuals are more likely to be uninsured, struggle to understand medical instructions, and avoid seeking care due to communication difficulties, which increases their risk of preventable hospitalizations and emergency room visits. Additionally, a BMC Health Services Research study found that communication barriers significantly contribute to longer hospital stays and higher readmission rates, adding financial strain to both patients and healthcare providers.
Language Access: Going Beyond Compliance
Federal policies such as Title VI of the Civil Rights Act and Executive Order 13166 require organizations receiving federal funding to provide language access services. Over time, the enforcement and implementation of these policies have evolved, with varying levels of oversight influencing how institutions approach language accessibility.
While government regulations establish a baseline for compliance, many organizations have taken proactive steps to expand language access services beyond federal requirements. They understand that integrating innovative language solutions, such as AI-powered interpretation, multilingual digital tools, and certified bilingual staff, enables them to improve service quality, enhance equity, and better serve diverse communities.
Language Access Plan Fundamentals
Language access plays a crucial role in improving service outcomes, enhancing customer experience, and fostering trust. Organizations that invest in robust language access plans can drive operational efficiencies, enrich public engagement, and gain a competitive advantage by reaching a broader and more diverse audience.
A strong language access plan that enables consistent service and improves quality includes the following elements:
- One company playbook: Clear organization-wide guidance that equips the workforce to operate efficiently, including policy, guidelines, workflows, training, metrics and performance reporting, preferred vendors with negotiated rates, source-of-truth decisions, sources for knowledge sharing, and an intake for prioritization of unmet needs.
- Certification for fluent employees: A clear and well-communicated path, often operated by HR, for employees to obtain certification as fluent employees to interpret on behalf of patients.
- On-demand workflow: A structured process for managing unmet language access requests, ensuring timely support by prioritizing and routing needs through a designated liaison. This system would adapt to changing demand and service channels by leveraging internal resources, preferred vendors, and evolving technologies.
- Digital tools: Solutions for knowledge management, employee certification, and triage management to provide redundancies and ensure maximum use of employees and overflow resources.
- Measurement: A short list of key performance indicators (KPIs) to track operational performance and customer feedback, enabling the organization to fine-tune services, calculate the return on investment, and prevent complaints.
Digital First: AI & Automation in Language Access
Advancements in digital technology have transformed language access in healthcare, enabling providers to deliver more seamless and equitable care with tools such as AI-driven translation, real-time interpreting, multilingual patient portals, and culturally responsive communication.
High-potentail technological advancements include:
- AI-powered translation and interpretation: Real-time translations, chatbots, and voice assistants improve interactions, with human oversight for high-risk situations.
- Automated customer communication: Multilingual content delivery across digital and physical channels ensures accurate and culturally relevant engagement.
- Digital accessibility & multilingual platforms: Patient portals, mobile apps, and legal service platforms now integrate multilingual interfaces to reduce friction points.
- AI and data analytics for continuous improvement: Predictive analytics help identify service gaps and refine language strategies for better engagement and efficiency.
These innovations streamline interpreter services and ensure that language is no longer a barrier to timely and effective treatment, fostering a more inclusive and patient-centered healthcare system. Organizations that integrate both human and technological solutions will create the most effective, inclusive, and high-impact language access strategies.
Key Questions to Get Started
A well executed language access plan is more than just a compliance requirement—it is a strategic asset that improves experiences and outcomes, and ensures equitable access to services. Organizations that proactively address language barriers can build trust and enhance operational efficiency.
To develop an effective and scalable language access service, organizations should ask:
- How do we measure performance and monitor needs related to language access services?
- What is the current level of patient satisfaction with our language services? Can we boost employee satisfaction by removing obstacles to meet patient needs?
- Does our frontline know how to easily and efficiently request interpreters and translation support?
- What languages are most prevalent among the communities we serve?
- How is our digital strategy evolving to address demand, and how are we leveraging AI?
- Do we have an enterprise-wide policy and guidelines for serving LEP customers?
- Who are our preferred vendors for over-the-phone interpretation (OPI), video remote interpretation (VRI), scheduled video interpretation (SVI), and translations? Do we have negotiated rates?
- What is our current spend rate with vendors, and how have costs been trending?
- Have we streamlined operations for OPI, VRI, and SVI with redundancies in place to improve experiences and mitigate risks?
- Are we maximizing and recognizing our workforce when they support interpreter services?
By addressing these key questions, organizations can create a structured approach to language accessibility, ensuring that all individuals—regardless of their language proficiency—receive the information and services they need in a clear, culturally relevant, and effective manner.
Ready to Eliminate Language Barriers?
Healthcare organizations have a significant opportunity to build a more inclusive system and ensure that language is never a barrier to critical services. A comprehensive approach enhances patient engagement, reduces medical errors, and improves care quality.
Are you ready to unlock new opportunities by enhancing language access? Please reach out, as we’d love to help. For more information on the future of work, culture, and innovation, follow Cortico-X on LinkedIn.

Robyn Gilson
is a Vice President at Cortico-X, leading our Healthcare practice. She leverages her vast CX and EX leadership expertise across industries to drive both cultural transformations and incremental growth for clients.

Edo Sayan
is a business transformation leader with expertise in financial services, payments, and healthcare. He has driven growth, customer experience, and multilingual strategies at Fortune 150 companies. Edo specializes in inclusive solutions that enhance engagement and business impact.











